Theme: Traversing the Future of Cell and Structural Biology
Cell Biologists Congress 2018


Welcoming Address to Participants of the “World Congress on Cell and Structural Biology 2018”.
In the spirit of traditional scientific exchange, via publications, international, national and regional meetings, class room lectures, as well as the use of current social media, the past and future of science has been and will be the exchange of ideas. That includes, not only exchanging shared interests, new technologies and findings but also, the challenging of prevailing paradigms. This is important, not only for the advance of science, in general, but how that science can help the quality of life and welfare of the world population.
In the context of today’s global situation of over population, ecological destruction, global warming, social unrest, wars, unequal distribution of wealth and resources, and destruction of traditional cultural values. By the end of this century, 3 billion new babies will be born. While these babies will have no choice in the genes they will inherit, they also will have no choice in the uterine environment that will influence their development and susceptibility to diseases later in life. This is due to the kinds of environments (dietary; psychological, social and cultural) we will provide all the pregnant women of the world. Even after birth, these children have little choice in the environments they find themselves. Witness the displacement of young children due to the wars of recent years.
Today, we are already beginning to see that non-infectious diseases are overtaking the scourges of infectious diseases that plagued humans in the past. Part of that might be attributed to a collision of glacier-slow biological evolution with the laser-speed Cultural evolution. In other words, rapid cultural changes are impacting on our genes that were acquired over millions of years to adapt to foods and cultural behavior practices of surviving in the jungle, desert, artic region, mountains, temperate and woods. Much of the global metabolic diseases (diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancers, etc.) are a result of the fact that rapid cultural changes ( diaspora of both peoples and foods; changing dietary practices; new food production, processing and distribution; economical/political choices, changing agricultural and animal production practices). This is creating major psychological, behavioral, social and cultural problems.
In no small way, we, as scientists, have a major ethical responsibility to help solve these complex problems. On one hand, we must continue doing science in the classical manner in being passionate about this unique human enterprise; being ethical in doing that science; and practice the exchange ideas as in this meeting. Yet that is not enough! As my late mentor, Dr. Van R. Potter (the person who coined the terms, “Bioethics” and “Global Bioethics”) stated in his American Association for Cancer Researchers Presidential Address [ “Humility with responsibility--a bioethic for oncologists”. Cancer Research, 1975) that it was not enough that we do and communicate good science to our peers, but we must be responsible to communicate that science to the public that sacrificed so that we do the science. Let us be frank. When the majority of the world’s population do not believe in evolution; know that we are existing in a galaxy that is one of billions; have no idea of DNA being the basis of our heredity; how radiation and chemicals can influence our health; and how the political choices to drive economies to grow certain foods, etc., we know we have not done our job in communicating our science in the broad ways it has changed, and is changing our existence and future.
Our course, science has no calculus to derive humane values. Values cannot be derived from science. However, human ethical values cannot ignore scientific facts. But for scientists to abrogate their responsibility to our traditional cultural non-scientific professionals (politicians; humanists, philosophers, religious leaders), that ignore scientific facts when choices must be made to use or not use scientific facts and technologies, we have let down our responsibility to use our expertise to improve the quality of all human beings.
Therefore, with this Address, I encourage all of us to do everything we traditionally do to improve our scientific disciplines, but also find ways in which our unique new scientific knowledge might be communicated to the wider general public.
We look forward to see you in Osaka, Japan.
James E. Trosko, Ph.D., Professor EmeritusCenter for Integrative Toxicology
Dept. Pediatrics/Human Development
College of Human Medicine
B207 Life Science Bldg
Michigan State University
Systems biology is the computational and mathematical modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological systems, using a holistic approach to biological research. Particularly from year 2000 onwards, the concept has been used widely in biology in a variety of contexts. The Human Genome Project is an example of applied systems thinking in biology which has led to new, collaborative ways of working on problems in the biological field of genetics. One of the outreaching aims of systems biology is to model and discover emergent properties, properties of cells, tissues and organisms functioning as a system whose theoretical description is only possible using techniques which fall under the remit of systems biology. Systems biology is the study of systems of biological components, which may be molecules, cells, organisms or entire species.
Related Conferences
9th International Conference on Structural Biology September 18-20, 2017 Zurich, Switzerland;2nd International Conference on Biochemistry September 28-29, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 10th International Conference and Exhibition on Metabolomics October 19-20, 2017 Baltimore, USA; International Conference on Next Generation Sequencing and Biostatistics October 23-24, 2018 Dubai; 3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9thInternational Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom
2. Structural and Cell Biology
Structural biology is a branch of molecular biology, biochemistry, and biophysics concerned with the molecular structure of biological macromolecules, especially amino and nucleic acids, how they acquire the structures they have, and how alterations in their structures affect their function. This subject is of great interest to biologists because macromolecules carry out most of the functions of cells, and only by coiling into specific three-dimensional shapes that they are able to perform these functions. This architecture, the "tertiary structure" of molecules, depends in a complicated way on the molecules' basic composition, or "primary structures." The cell is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and cells are often called the building blocks of life. The study of cells is called cell biology. Cell biology is a branch of biology that studies the different structures and functions of the cell and focuses mainly on the idea of the cell as the basic unit of life. Cell biology explains the structure, organization of the organelles they contain, their physiological properties, metabolic processes, Signaling pathways, life cycle, and interactions with their environment. This is done both on a microscopic and molecular level as it encompasses prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences; it is also essential for research in bio-medical fields such as cancer, and other diseases. Research in cell biology is closely related to genetics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, and developmental biology.
Related Conferences
Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France; 19th International Conference on Structural Biology Toronto, Canada June 15 - 16, 2017; International Conference on Clinical and Medical Genetics September 21-22, 2017 Toronto, Canada; Annual Summit on Cell Therapy and Molecular Medicine September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; Annual Summit on Cell Signaling and Cancer Therapy September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; 10th World Congress on Stem Cell and Bio banking October 23-24, 2017 Osaka, Japan
3. Bio Physics and Structural Biology
Biophysics or biological physics is an interdisciplinary science that applies the approaches and methods of physics to study biological systems. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, physical chemistry, nanotechnology, Bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics and systems biology. Molecular biophysics typically addresses biological questions similar to those in biochemistry and molecular biology, seeking to find the physical underpinnings of bimolecular phenomena. Structural biology is the study of the molecular structure and dynamics of biological macromolecules, particularly proteins and nucleic acids, and how alterations in their structures affect their function. Structural biology incorporates the principles of molecular biology, biochemistry and biophysics. Structural biology seeks to provide a complete and coherent picture of biological phenomena at the molecular and atomic level. The goals of structural biology include developing a comprehensive understanding of the molecular shapes and forms embraced by biological macromolecules and extending this knowledge to understand how different molecular architectures are used to perform the chemical reactions that are central to life.
Related Conferences
3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France; 19th International Conference on Structural Biology Toronto, Canada June 15 - 16, 2017; International Conference on Clinical and Medical Genetics September 21-22, 2017 Toronto, Canada
Structural biochemistry is a branch of the life sciences that combines biology, physics, and chemistry to study living organisms and to summarize some mutual principles that all forms of life share. Biochemists aim to describe in molecular terms the structures, mechanisms, and chemical processes shared by all organisms, providing organizing principles that underlie life in all its diverse forms. Structural Biochemistry is a subdivision of biochemistry mainly focused on the components, structures and functions of molecules within cells that make up the living organisms. Biochemistry attempts to explain the phenomenon of life in chemical terms by using various theories in Chemistry and the laws of Physics. The general theme that underlies the work of the structural biochemistry is macromolecular structural and functional biochemistry in which protein structures and protein interactions within complexes in solution are used as the starting point for further studies on the mechanisms of catalysis, mechanisms of inhibition, regulation, molecular recognition, and structure-based drug design. The Structural biochemistry serves the educational and research needs in the disciplines of biochemistry , structural biochemistry, proteomics, structural genomics, regulation and Metabolic Control of Enzymes and the implementation of all the above in Analytical Biochemistry, Enzymology, Clinical Biochemistry, Food biochemistry, Chemical Biology, structure-driven drug design and Biophysics as applied to Biochemical Sciences.
Related Conferences
9th International Conference on Structural Biology September 18-20, 2017 Zurich, Switzerland;2nd International Conference on Biochemistry September 28-29, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 10th International Conference and Exhibition on Metabolomics October 19-20, 2017 Baltimore, USA; International Conference on Next Generation Sequencing and Biostatistics October 23-24, 2018 Dubai; 3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom
Bio-engineering is the application of concepts and methods of biology to solve real-world problems related to life sciences or the application thereof, using engineering's own analytical and synthetic methodologies and also its traditional sensitivity to the cost and practicality of the solution arrived at. Biological engineering uses primarily the rapidly developing body of knowledge known as molecular biology to study and advance applications of organisms and to create biotechnology. This may eventually include the possibility of biologically engineering machines and 3D printing that re-order matter at a molecular scale. Industrial bio-engineering extends from the creation of artificial organs by technical means or finds ways of growing organs and tissues through the methods of regenerative medicine to compensate reduced or lost physiological functions and to develop genetically modified organisms, i.e., agricultural plants and animals as well as the molecular designs of compounds with desired properties (protein engineering, engineering enzymology). In the non-medical aspects of bio-engineering, it is closely related to biotechnology, nanotechnology and 3D printing.
Related Conferences
Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France; 19th International Conference on Structural Biology Toronto, Canada June 15 - 16, 2017; International Conference on Clinical and Medical Genetics September 21-22, 2017 Toronto, Canada; Annual Summit on Cell Therapy and Molecular Medicine September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; Annual Summit on Cell Signaling and Cancer Therapy September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; 10th World Congress on Stem Cell and Bio banking October 23-24, 2017 Osaka, Japan
Chemical biology is a scientific discipline spanning the fields of chemistry, biology, and physics. It involves the application of chemical techniques, tools, and analyses, and often compounds produced through synthetic chemistry, to the study and manipulation of biological systems. Chemical biologists attempt to use chemical principles to modulate systems to either investigate the underlying biology or create new function. Chemical biology studies probe systems in vitro and in vivo with small molecules that have been designed for a specific purpose or identified on the basis of biochemical or cell-based screening. Chemical biology has scientific, historical and philosophical roots in medicinal chemistry, supra molecular chemistry (particularly host-guest chemistry), bioorganic chemistry, pharmacology, genetics, biochemistry, and metabolic engineering. Chemical biology is the study of the chemicals and chemical reactions involved in biological processes, incorporating the disciplines of bioorganic chemistry, biochemistry, cell biology and pharmacology. An important thrust area is Chemical Biology which combines the fields of synthetic chemistry, molecular biology, and molecular imaging, to create novel chemical tools for probing biological systems.
Related Conferences
3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France; 19th International Conference on Structural Biology Toronto, Canada June 15 - 16, 2017; International Conference on Clinical and Medical Genetics September 21-22, 2017 Toronto, Canada
7. Computational Structural Biology
Computational structural biology has made tremendous progress over the last two decades. Computational structural biology has impact on protein structure prediction methods, macromolecular function and protein design, and key methods in drug discovery. It also addresses the computational challenges of experimental approaches in structural biology. Computational Structural Biology aims at establishing bio molecular sequence-structure-function relations using fundamental principles of physical sciences in theoretical models and simulations of structure and dynamics. After the advances in complete genomes sequencing, it became evident that structural information is needed for understanding the origin and mechanisms of biological interactions, and designing/controlling function. Computational Structural Biology emerged as a tool for efficient identification of structure and dynamics in many applications. Major research topics include protein folding, protein dynamics with emphasis on large complexes and assemblies, protein-protein, protein-ligand and protein-DNA interactions and their functional implications. Drug design and protein engineering represent applications of note. Computational structural biology studies aspects of bio molecular structure and dynamics by means of computational methods. The group's focus is on tool development for bio molecular structure determination, prediction and modeling.
Related Conferences
10th International Conference and Exhibition on Metabolomics October 19-20, 2017 Baltimore, USA; International Conference on Next Generation Sequencing and Biostatistics October 23-24, 2018 Dubai; 3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France
8. Structural Biology in Drug Discovery
Rational drug design aims to develop small molecules (drugs) with a therapeutic effect by targeting biomolecules in order to influence their biological function. Structural biology has a diverse arsenal of methods available to study (bio) molecular structures. Information on the shape and possible interaction sites of binding sites on these molecules can be used to design small molecules with high binding affinity. The structural information is a valuable input in different stages of drug development such as lead optimization or drug design. Structural determination of bio molecules could serve as therapeutic target is an important starting point in rational drug design. Once the structure of a biological target is known, a potential binding site for drugs and possible interactions at this site have to be identified in the stage of drug design.
Related Conferences
9th International Conference on Structural Biology September 18-20, 2017 Zurich, Switzerland;2nd International Conference on Biochemistry September 28-29, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 10th International Conference and Exhibition on Metabolomics October 19-20, 2017 Baltimore, USA; International Conference on Next Generation Sequencing and Biostatistics October 23-24, 2018 Dubai; 3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom
9. Data Mining in Structural Biology
Data mining is the computing process of discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. It is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science. The overall goal of the data mining process is to extract information from a data set and transform it into an understandable structure for further use. Aside from the raw analysis step, it involves database and data management aspects, data pre-processing, model and inference considerations, interestingness metrics, complexity considerations, post-processing of discovered structures, visualization, and online updating. Data mining is the analysis step of the "knowledge discovery in databases" process, or KDD. The actual data mining task is the semi-automatic or automatic analysis of large quantities of data to extract previously unknown, interesting patterns such as groups of data records, unusual records , and dependencies . Multi-relational data mining tools have been applied to a variety of biological tasks. Biological data bases provide a major challenge for multi-relational data mining. Already, data mining researches should be more ambitious in applying multi-relational algorithms to larger and more diverse databases.
Related Conferences
Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France; 19th International Conference on Structural Biology Toronto, Canada June 15 - 16, 2017; International Conference on Clinical and Medical Genetics September 21-22, 2017 Toronto, Canada; Annual Summit on Cell Therapy and Molecular Medicine September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; Annual Summit on Cell Signaling and Cancer Therapy September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; 10th World Congress on Stem Cell and Bio banking October 23-24, 2017 Osaka, Japan
10. Nano Engineering
Nano engineering is the practice of engineering on the Nano scale. It derives its name from the nanometer. Nano engineering is largely a synonym for nanotechnology, but emphasizes the engineering rather than the pure science aspects of the field. Nanotechnology Engineering is a multi-disciplinary engineering field, which draws from and benefits areas such as materials science and engineering, chemistry, physics, biology, and medicine. Nanotechnology is becoming the driving force behind a variety of evolutionary and revolutionary changes in the medical field. Nano scale sciences program investigates problems at the interface of engineering, biology, and nanotechnology, allowing us to apply the fundamental principles of mechanical engineering to expand opportunities for new science and engineering breakthroughs. By merging the engineering fields of dynamics, materials, mechanics, fluid flow, and heat transfer with the scientific fields of chemistry, materials science, and biology, we pursue experimental and computational strategies to understand the physical principles specific to small scale and biological phenomena. This enabling research uses unique physics at the nanometer scale with a view toward revolutionizing areas such as biomedicine and biotechnology.
Related Conferences
3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France; 19th International Conference on Structural Biology Toronto, Canada June 15 - 16, 2017; International Conference on Clinical and Medical Genetics September 21-22, 2017 Toronto, Canada
11. Neurobiology
Neurobiology is the study of cells of the nervous system and the organization of these cells into functional circuits that process information and mediate behavior. Neurobiology is the study of the brain and nervous system, which are the cells and tissue that generate sensation, perception, movement, learning, emotion, and many of the functions that make us human. Neurobiology is intrinsically multi-disciplinary, spanning from molecular biology and gene regulation in neurons, to chemical and electrical signaling in neurons, to information processing by neural circuits and brain regions, to nervous system development and plasticity.
Related Conferences
10th International Conference and Exhibition on Metabolomics October 19-20, 2017 Baltimore, USA; International Conference on Next Generation Sequencing and Biostatistics October 23-24, 2018 Dubai; 3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France
12. Stem cell biology and Regenerative medicine
Stem cells are undifferentiated biological cells that can differentiate into specialized cells and can divide to produce more stem cells. There is great interest in stem cells because they have potential in the development of therapies for replacing defective or damaged cells resulting from a variety of disorders and injuries, such as Parkinson disease, heart disease, and diabetes. The discovery of stem cells has opened new possibilities for the treatment of these maladies, and cell therapy now stands at the cutting-edge of modern regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Regeneration is the process of renewal, restoration, and growth that makes genomes, cells, organisms, and ecosystems resilient to natural fluctuations or events that cause disturbance or damage. Regenerative medicine is a branch of translational research in tissue engineering and molecular biology which deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function". Regenerative medicine also includes the possibility of growing tissues and organs in the laboratory and implanting them when the body cannot heal itself. Some of the biomedical approaches within the field of regenerative medicine may involve the use of stem cells. Regenerative medicine is a broad field that includes tissue engineering but also incorporates research on self-healing – where the body uses its own systems, sometimes with help foreign biological material to recreate cells and rebuild tissues and organs
Related Conferences
Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France; 19th International Conference on Structural Biology Toronto, Canada June 15 - 16, 2017; International Conference on Clinical and Medical Genetics September 21-22, 2017 Toronto, Canada; Annual Summit on Cell Therapy and Molecular Medicine September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; Annual Summit on Cell Signaling and Cancer Therapy September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; 10th World Congress on Stem Cell and Bio banking October 23-24, 2017 Osaka, Japan
Cardiac cell biology has come of age Cutting edge technological advances and aplethora of specialized reagents to allow the study and understanding of cells of heart cells to an unprecedented level. Cardiac hypertrophy in all its complexity remains a fundamental goal of cardiac research.
Related Conferences
Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France; 19th International Conference on Structural Biology Toronto, Canada June 15 - 16, 2017; International Conference on Clinical and Medical Genetics September 21-22, 2017 Toronto, Canada; Annual Summit on Cell Therapy and Molecular Medicine September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; Annual Summit on Cell Signaling and Cancer Therapy September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; 10th World Congress on Stem Cell and Bio banking October 23-24, 2017 Osaka, Japan
14. Cancer Biology
Cancer biology focuses on the mechanisms that underlie fundamental processes such as cell growth, the transformation of normal cells to cancer cells, and the spread, or metastasis, of cancer cells. The biology of cancer is studied at many levels and in many organisms, ranging from the discovery of genes implicated in the development of cancer in humans to the elucidation of basic cell biological processes that are affected during tumorigenesis, which can be studied using human cells as well as model organisms. Investigations in the Cancer Biology department include studies on the tumor microenvironment, metastasis, angiogenesis, apoptosis, cell adhesion, gene expression, transcription, invasion, tumor suppressor genes, oncogenes, cancer stem cells, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, signaling, immunotherapy, biomarkers, resistance to therapy and tumor modeling.
Related Conferences
9th International Conference on Structural Biology September 18-20, 2017 Zurich, Switzerland;2nd International Conference on Biochemistry September 28-29, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 10th International Conference and Exhibition on Metabolomics October 19-20, 2017 Baltimore, USA; International Conference on Next Generation Sequencing and Biostatistics October 23-24, 2018 Dubai; 3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom
15. Immunology
Immunology is a branch of biology that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms. It was an active response of the body, trying to maintain its integrity. Many components of the immune system are typically cellular in nature and not associated with any specific organ; but rather are embedded or circulating in various tissues located throughout the body. Classical immunology ties in with the fields of epidemiology and medicine. It studies the relationship between the body systems, pathogens, and immunity. Clinical immunology is the study of diseases caused by disorders of the immune system. It also involves diseases of other systems, where immune reactions play a part in the pathology and clinical features. Immunology is a branch of biomedical science that covers the study of all aspects of the immune system in all organisms. It deals with the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the immune system in vitro, in situ and in vivo.
Related Conferences
10th International Conference and Exhibition on Metabolomics October 19-20, 2017 Baltimore, USA; International Conference on Next Generation Sequencing and Biostatistics October 23-24, 2018 Dubai; 3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France
16. NMR and Mass Spectroscopy
NMR spectroscopy is a very powerful tool to study structure and dynamics with atomic resolution. The workshop in NMR consists of lectures and practical sessions at basic , advanced and specialized levels with topics covering Structure Determination of Biomolecules, Checking synthesized substances and identify compounds isolated from natural sources, Drug Screening, NMR in Proteomics and Metabolomics: Basic Information; Biomarkers, Dynamics: Molecules, Enzymatic Reactions – Kinetics, Molecular Interactions: Protein-Protein, Protein-DNA, Drug-Target Protein etc… NMR spectroscopy is a powerful tool for biologists interested in the structure, dynamics and interactions of biological macromolecules. NMR is suitable to monitor, over a wide range of frequencies, protein fluctuations that play a crucial role in their biological function. Native mass spectrometry gives information about the composition, topological arrangements, dynamics, and structural properties of protein complexes. The mass range is principally unlimited and highly dynamic, allowing the detection of small subunits and large complexes within the same measurement. Mass spectrometry is the one that provide lower resolution, but critical, structural information with high throughput. We use “native” mass spectrometry in a collaborative approach as a tool for structural biology, to elucidate the subunit composition, stoichiometry, stability and dynamics of functional protein-protein and protein-DNA/RNA complexes which have been recombinant expressed or isolated from cells.
Related Conferences
Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France; 19th International Conference on Structural Biology Toronto, Canada June 15 - 16, 2017; International Conference on Clinical and Medical Genetics September 21-22, 2017 Toronto, Canada; Annual Summit on Cell Therapy and Molecular Medicine September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; Annual Summit on Cell Signaling and Cancer Therapy September 27-28, 2017 Chicago, Illinois, USA; 10th World Congress on Stem Cell and Bio banking October 23-24, 2017 Osaka, Japan
17. Future Scope of Cell and Structural Biology
The emergence of the new fields of structural genomics and functional genomics presents us with an unprecedented availability of new macromolecules with so far unknown functions and the promise of novel insights into the mode of action of intact organisms. Technical advances made over several decades have enabled researchers to determine the structures of increasingly larger molecules and complexes, including the protein-making ribosome—a molecular behemoth composed of several RNA molecules and dozens of proteins and the target of many antibiotics. Today, scientists are using high-throughput methods to determine protein structures more quickly than ever before. They are also using computational techniques to predict three-dimensional structures of proteins of unknown structure and to design new proteins with useful functions. This work will continue to increase our understanding of the diverse roles molecules play in biology and to spur advances in medicine. We envision the cell as a little universe in which a multitude of molecular processes occur, recapitulating most of the basic processes of life. The cell functions as an operation center, which integrates all the possible “omics” (genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, glycomics, exposomics, etc.) to generate context-dependent responses that allow cells to adapt and relate to their surrounding milieu. Owing to the central role of the cell, the tremendous technological progress and the development in systems biology, we are now well positioned to study cell biology and genetics as a whole and translate the enormous potential of these findings to all the possible settings.
Related Conferences
10th International Conference and Exhibition on Metabolomics October 19-20, 2017 Baltimore, USA; International Conference on Next Generation Sequencing and Biostatistics October 23-24, 2018 Dubai; 3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom; Nuclear structure and dynamics 04 – 08 October 2017 | L'Isle sur la Sorgue, France
18. Regulations and Ethics
The field of bioethics has addressed a broad swathe of human inquiry, ranging from debates over the boundaries of life, surrogacy, and the allocation of scarce health care resources to the right to refuse medical care for religious or cultural reasons. Bioethicists often disagree among themselves over the precise limits of their discipline, debating whether the field should concern itself with the ethical evaluation of all questions involving biology and medicine, or only a subset of these questions. Some bioethicists would narrow ethical evaluation only to the morality of medical treatments or technological innovations, and the timing of medical treatment of humans. Others would broaden the scope of ethical evaluation to include the morality of all actions that might help or harm organisms capable of feeling fear. The scope of bioethics can expand with biotechnology, including cloning, gene therapy, life extension, human genetic engineering, astroethics and life in space, and manipulation of basic biology through altered DNA, RNA and proteins. These developments will affect future evolution, and may require new principles that address life at its core, such as biotic ethics that values life itself at its basic biological processes and structures, and seeks their propagation. One of the first areas addressed by modern bioethicists was that of human experimentation. Another important principle of bioethics is its placement of value on discussion and presentation. Bioethics has a more expansive application, touching upon the philosophy of science and issues of biotechnology. A bioethicist assists the health care and research community in examining moral issues involved in our understanding of life and death, resolving ethical dilemmas in medicine and science.
Related Conferences
9th International Conference on Structural Biology September 18-20, 2017 Zurich, Switzerland;2nd International Conference on Biochemistry September 28-29, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 10th International Conference and Exhibition on Metabolomics October 19-20, 2017 Baltimore, USA; International Conference on Next Generation Sequencing and Biostatistics October 23-24, 2018 Dubai; 3rd International Conference on Transcriptomics October 30 - November 01, 2017 Bangkok, Thailand; 9th International Conference and Expo on Proteomics November 13-15, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Genetic and Protein Engineering November 08-09, 2017 Las Vegas, USA; 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics November 13-14, 2017 Paris, France; 3rd International Conference on Lipid Science & Technology December 11-12, 2017 Rome, Italy; Eukaryotic RNA turnover 10 – 13 July 2017 | Oxford, United Kingdom
We welcome all the participants to the World Congress on Cell and Structural Biology going to be held during May 14-15 at Osaka, Japan.
We invite all the cell and structural biologists, alternative and complementary biology practitioners, researchers in the field of cell and molecular biology, Biochemistry, Genetics, Immunology, Microbiologists, people to explore their research, at cell and structural biology conference 2018 in Osaka, Japan.
Cell and Structural Biology Congress 2018 anticipates hundreds of delegates including international keynote lectures and oral presentations by renowned speakers and poster presentations by students, and delegates all around the world which will craft a platform for global promotion of several techniques. It provides international networking and opportunities for collaborations with worldwide companies and industries.
We are sure Cell and Structural Biology 2018 will be an incredible open door for the global group to trade thoughts and add to a typical vision for future research and prompts collaboration among researchers taking an interest.
Summary of Cell and Structural Biology Conference:-
The Cell Biology, structural Biology & molecular modelling techniques market is expected to reach USD 13.1 billion by 2025. Increasing drug resistance coupled with the high drug attrition rate is engendering the requirement for extensive R&D activities, which is presumed to boost the adoption of Cell and structural biology & molecular modelling techniques in the drug discovery and development process. This is expected to serve as an efficient approach in fast tracking the development of drugs with high potency.
The heightening demand For Cell and Structural Biology and Molecular modelling techniques is predominantly attributable to the significant cost reduction enabled. This is due to the fact that prediction software identifies possible adverse reactions and determines drug efficacy and toxicity in the pre-clinical stages, thereby reducing the probability of drug failure at the later stages. Consequentially, the aforementioned factors serve as prominent reasons responsible for the widened market demand.
Scope and Importance
Technical advances made over several decades have enabled researchers to determine the structures of increasingly larger molecules and complexes, including the protein-making ribosome—a molecular behemoth composed of several RNA molecules and dozens of proteins and the target of many antibiotics. Today, scientists are using high-throughput methods to determine protein structures more quickly than ever before. They are also using computational techniques to predict three-dimensional structures of proteins of unknown structure and to design new proteins with useful functions.
We envision the cell as a little universe in which a multitude of molecular processes occur, recapitulating most of the basic processes of life. The cell functions as an operation center, which integrates all the possible “omics” (genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, glycomics, exposomics, etc.) to generate context-dependent responses that allow cells to adapt and relate to their surrounding milieu. Owing to the central role of the cell, the tremendous technological progress and the development in systems biology, we are now well positioned to study cell biology and genetics as a whole and translate the enormous potential of these findings to all the possible settings.
Why to Attend Cell and Structural Biology Conference 2018
World Congress on Cell and Structural Biology going to be held from May 14-15, 2018, at Osaka, Japan is going to be the biggest conference dedicated to Cell and Structural Biology fraternity. It provides a premier technical forum for reporting and learning about the latest research and development, along with discussing new applications and technologies. Events include hot topics presentations from all over the world and professional networking with industries, leading working groups and panels.
Cell Biologists Congress 2018 anticipates hundreds of delegates including international keynote lectures and oral presentations by renowned speakers and poster presentations by students, and delegates all around the world which will craft a platform for global promotion of safe and effective natural therapies. It provides international networking and opportunities for collaborations with worldwide companies and industries.
Cell and Structural Biology 2018 will be a global platform for sharing information and ability from both scientific and industrial group. The meeting goes for uniting the academicians, scientists, instructors, business pioneers, investors and young researchers to a global stage where they can showcase their novel research and contributions in the field of Cell and structural biology and biophysics.
Best platform to develop new partnership & collaborations | Best location to speed up your route into every territory in the World | 89% our conference attendees are the Key contact in their labs purchasing decisions | Our exhibitor booths were visited 4-5 times by 80% of the attendees during the conference | Past exhibitor’s feedback reveals ample of enquiries perceived from the conference attendees | Network development with both Academia and Business
Why in Japan
The Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP), which funds basic research in the areas of molecular and cell biology and brain research was launched in 1989 following an initiative by the then prime minister of Japan, Yasuhiro Nakasone. The program was initiated at a time when Japan's economy was flourishing but its scientific research seemed isolated from Western countries. The primary aim of the program was, therefore, to promote basic biological research at an international level, and at the same time to provide an opportunity for Japanese researchers to collaborate more closely with scientists in other countries.
Until 1992, almost all of the US$30 billion annual budget was provided by the Japanese government. Although, in 1992, it was accepted that contributions to the program from the countries that benefit from it should be more equal, Japan still pays the lion's share (around 75% of the $47 billion yearly budget). While it may seem hard to understand why a single country is funding the bulk of this program while receiving no bigger (and often smaller) a share than other countries, most Japanese researchers to whom we have spoken welcomed the program as "one of the best policies the Japanese government has ever invested into science". Most praise the contribution the program has made to promote Japanese science and its recognition in the international scientific community, as well as the personal contacts and collaborations it has allowed. Importantly, Japan's partners have agreed to increase their shares gradually until the year 2002, allowing the total budget to grow to $60 billion.
Who should attend?
Biochemists | Biotechnologists | Bioinformatics | Cell Biologists | Developmental Biologists | Geneticists |Micro Biologists | Molecular Biologists | System Biologists | Immunologists | Biophysicist | Structural biologists | Bioengineering | Nano engineering | Neuro Biologist | Computational Biologist
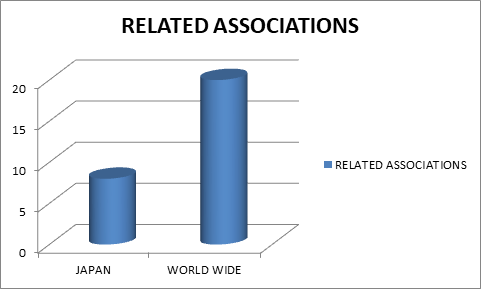
Societies Associated with Cell and Structural Biology Research:-
Country wise Statistics (Japan):-
NARA Institute of Science and Technology | Research Institute for Biomedical Sciences | National Institute for Basic Biology | Center for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine | Japan Society for Cell Biology | Nakano Laboratory
Worldwide Statistics (International):-
Indian Society of Cell Biology | American Society for Cell Biology | American Society of Cytopathology | Cell Death and Apoptosis: The Cell Death Society | International Federation for Cell Biology | Association of Bio molecular Resource Facilities | International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology | Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology | Society for Developmental Biology | American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB) | British Society for Cell Biology | The Biochemical Society | American Association of Immunologists | Clinical Immunology Society | British Society for Immunology | Czech Society for Structural Biology | Biophysical Society | American Chemical Society | New England Structural Biology Association | The Protein Society | American Crystallographic Association | International Union of Crystallography | British Crystallographic Association | European Crystallographic Association | Hellenic Crystallographic Association | Bioinformatics society of India | International Society for Computational Biology | South African Crystallographic Society | Australian Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology | Australian Society for Biophysics | American Society for Mass Spectrometry | British Biophysical Society | Bioinformatics Italian Society | Mid-South Computational Biology and Bioinformatics Society
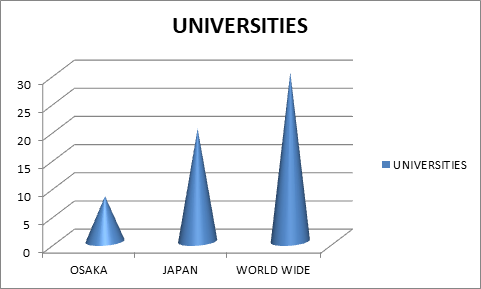
Universities Associated with Cell and Structural Biology Research:-
List of Universities in Osaka:
Osaka University | Osaka Jogakuin University | Osaka City University
List of Universities in Japan:
University of Tokyo | Kyoto University | Tohoku University | Kyushu University | Nagoya University | University of Tsukuba | Keio University | Tohoku University | Kobe University | Hiroshima University | Hokkaido University| Medical College Of Ohio
List of Universities in the World:
Harvard University | University of California | University of Cambridge | Stanford University | University of Washington | University of Oxford | Johns Hopkins University | University of Toronto | University of Rhode | The University Of Sheffield | Quinnipiac University | Uniformed Services University | Emory University | New York Medical College | Baylor College of Medicine | Rice University | Brock University | New Mexico State University | Oregon State University | University of Skovde | Miami University | Fordham University
Industries Associated with Cell And Structural Biology Research:
MyBioSource | Freudenberg Medical | Progen | Sirion Biotech | Aurinia Pharmaceuticals | KMT Hepatech | Dilyx Biotechnologies (Soluble Therapeutics) | Evonik Industries | SouthernBiotech | Vivo BioSciences | Conversant Bio | Genea Biocells | Elastagen | Invitrogen | TGR BioScience | GE Healthcare | Applied Biological Materials | JSR Life Sciences | Caribou Biosciences | BioGenex | Mandala Biosciences
Market Value on Cell and Structural Biology:-
The top 10 cellular analysis market is expected to reach USD 41.34 Billion by 2021 from USD 28.66 Billion in 2016, at a CAGR of 7.6% from 2016 to 2021. The major factors driving the growth of this market are the growing biotechnology and biopharmaceutical industries, introduction of technologically advanced cell analysis instruments, increasing incidence of infectious and chronic diseases and rising number of patients suffering from cancer, and increasing investments from various government associations & life sciences companies for cell biology research activities.
The market is mainly driven by the increasing research funding for structural biology from governments and private investors, growing demand for novel drug design and personalized medicine in the U.S. and Europe, and the increasing need for toxicology testing. The presence of a large number of analytical equipment manufacturers has contributed significantly to the North American and European structural biology/drug market. However, the Asia-Pacific region represents a significant growth opportunity for the structural biology/drug market during the forecast period of 2014 to 2019. The APAC market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 23% during the forecast period. The growth in this market is driven by the growing pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. The global structural biology market was valued at $565 million in 2014 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 30% from 2014 to 2019.
Funds allotted to Cell and Structural Biology Research:-
The Higher Education Funding Council for England (HEFCE), the agency responsible for the distribution of almost £8 billion (US$11.3 billion) of government funds for the academic year 2009–10, unveiled provisional funding allocations for research (£1.57 billion) and teaching (£4.78 billion). NIH spends approximately $65 million each year for protein structure determination. Australia grants worth $7.4 million for 14 national projects supporting the growth of the medical technologies, biotechnologies and pharmaceuticals sector. The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)—the leading official body in coordinating and funding science and technology initiatives in Japan—requested US$11.1 billion for science and technology spending in its proposed budget. National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), Prevention Research, has funded $358.1 million in 2015. The state of California, has reportedly invested $10-12 million in direct cancer research annually, while the National Cancer Institute (NCI) within the United States has reportedly spend $4.8 to $5.2 billion per annum on cancer research and treatment development. With the recent request for applications, the NIGMS expects to support three to six large research centers at a level of up to $3 million per center.
ABOUT CITY
Japan is prosperous organizations in the nation Furthermore need the mossy cup oak different economy for Asia. The welcome spring may be gentle also acquires out Japan’s acclaimed cherry blossoms. The middle of the year begins with the blustery season to late June alternately promptly July. Osaka castle will be Japanese manor in Japan. The palace will be a standout amongst Japan's practically celebrated point of interest Also it assumed a major part in the unification from claiming japan.
Osaka is a large port city and commercial center on the Japanese island of Honshu. It's known for its modern architecture, nightlife and hearty street food. The 16th-century shogunate Osaka Castle, which has undergone several restorations, is its main historical landmark. It's surrounded by a moat and park with plum, peach and cherry-blossom trees. Sumiyoshi-taisha is among Japan’s oldest Shinto shrines.
Conference Highlights
- Systems Biology
- Structural and Cell Biology
- Bio Physics and Structural Biology
- Structural Biochemistry
- Bio-Engineering
- Chemical Biology
- Computational Structural Biology
- Structural Biology in Drug Discovery
- Data Mining in Structural Biology
- Nano Engineering
- Neurobiology
- Stem cell biology and Regenerative medicine
- Cardiac cell biology
- Cancer Biology
- Immunology
- NMR and Mass Spectroscopy
- Future Scope of Cell and Structural Biology
- Regulations and Ethics
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | May 14-15, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- 1. Cell & Developmental Biology
- 2. Biochemistry & Molecular Biology Journal
- 3. Journal of Proteomics & Bioinformatics
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by